Introduction | Get Started | Learn | Practice | Apply | Explore Further | Checkpoint
Download the checklist for a new product development commercialization plan.
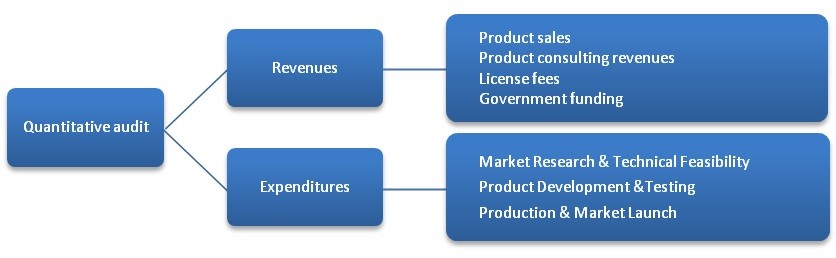
A critical consideration for the effective use of a costing model is a realistic projection of revenue and expenditures. Under revenues, it is necessary to have a good understanding of the viability of the product and the sources of funding for the new chocolate food product. While projected product sales will be the top consideration for the product launch, there may be other considerations such as government funding, license fees, etc. to be taken into account. Under expenditures, three important considerations have been identified: Market Research & Technical Feasibility, Product Development & Testing and Production & Market Launch.
Why is Revenue important for your innovation project?
In business, revenue is income that a company receives through its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and/or services to customers. There are times when revenue may be referred to as turnover. Some companies receive revenue from interest, royalties, or other fees.
Revenue may be used to refer to business income in general, or it may refer to the amount, expressed in a monetary unit, received during a period of time, as in “Last year, Company X had revenue of $44 million.” Profits or net income generally imply total revenue less total expenses in a given period. In accounting terminology, revenue is often referred to as the “top line” due to its position on the income statement at the very top. This is in relation to the “bottom line” which denotes net income.
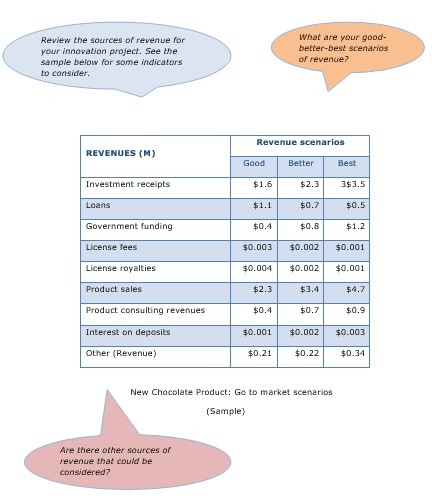
Under revenues, it is important to have a good understanding of the viability of the product and the sources of funding for an initiative such as a new chocolate food. Clearly product sales in the list below will be the top consideration for the product launch.
- Investment receipts
- Loans
- Government funding
- License fees
- License royalties
- Product sales
- Product consulting revenues
- Interest on deposits
- Other
Innovation Costing – Capacity Review
To understand the readiness of your organization and team to move forward with a costing for your innovation project, you first need to do a capacity review. Please review the four criteria of the capacity review and answer the questions under each one.

New household cleaning product: Capacity Review
Based on an capacity review assessment of the management, market, technical and financial capacities of the organization, the chart shows the areas where the organization has strengths and identifies areas where there are gaps.
The capacity assessment within the qualitative audit provides a good overview of the viability of the new household cleaning food product and will identify the “current state” of the initiative and as well as offering insight into what is needed to succeed in the market. As a result, the management and product development team can take steps to address potential gaps in the innovation cycle. They can also increase the emphasis on areas where there may be a need for a concerted effort to mitigate the risk associated with unpredictable situations in the development process.
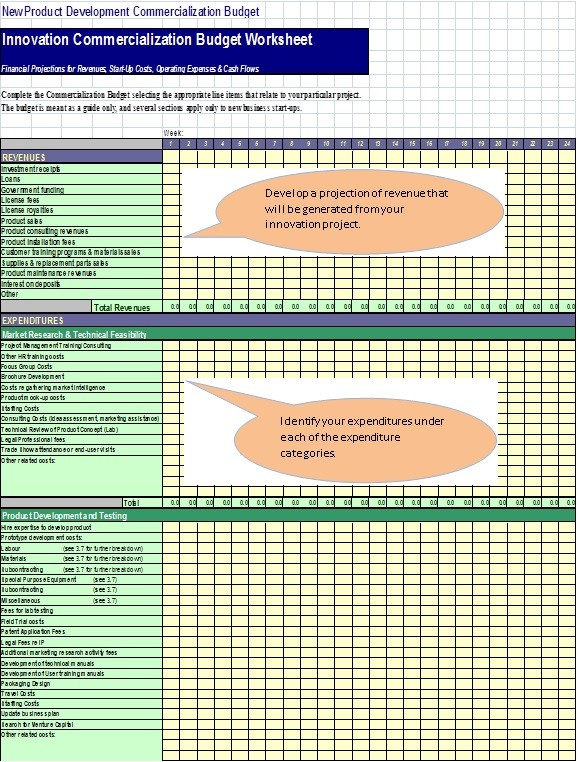
New Product Development Commercialization Budget

Once you have completed your capacity assessment, you will need to develop a budget for your innovation project. Below is an innovation commercialization budget worksheet for your use. (Click on image to download the Excel version of the New Product Development Commercialization Budget worksheet).
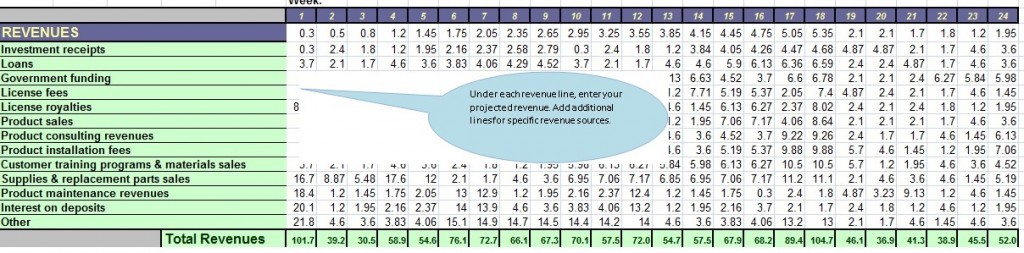
STEP 1: What is your revenue projection?
In general usage, revenue is income received by an organization in the form of cash or cash equivalents. Sales revenue is income received from selling goods or services over a period of time. Tax revenue is income that a government receives from taxpayers. In more formal usage, revenue is a calculation or estimation of periodic income based on a particular standard accounting practice or the rules established by a government or government agency.
TIP: Two common accounting methods, cash basis accounting and accrual basis accounting, do not use the same process for measuring revenue.
In the sample costing below for a household cleaning product, the revenue projection ranges from $30k to $104k.
What is Business Revenue?
Business Revenue is income from ordinary activities for a particular organization. For some businesses, such as manufacturing and/or grocery, most revenue is from the sale of goods. Service businesses such as law firms and hair salons receive most of their revenue from rendering services. Lending businesses such as car rentals and banks receive most of their revenue from fees and interest generated by lending assets to other organizations or individuals.
Revenues from the primary activity of a business are reported as sales, sales revenue or net sales. This includes accounting for product returns and discounts for early payment of invoices. Most businesses also have revenue that is incidental to the business’s primary activities, such as interest earned on deposits in a demand account. This sum is included in revenue but not included in net sales. Sales revenue does not include any sales tax collected by the business. Other revenue (a.k.a. non-operating revenue) is revenue from peripheral (non-core) operations. For example, a company that manufactures and sells automobiles would record the revenue from the sale of an automobile as “regular” revenue. If that same company also rented a portion of one of its buildings, it would record that revenue as “other revenue” and disclose it separately on its income statement to show that it is from something other than its core operations.
What type of Innovation are you considering?
The first step in the costing process is to define the type of innovation the new household cleaning product can be classified under. There are three broad types of innovation: incremental, substantial and transformational. Incremental Innovation is the most common and features the introduction of a product involving some level of “newness” and some value creation. An example is a “new and improved” type of household cleaning product variant such as a new scent.
Substantial Innovation is where there is a significant degree of product originality and important value creation for the customer. An example is a new form such as a concentrated formula required reduced packaging. Transformational Innovation is the least common and involves radical new products that create substantial value for the customer. An example would be the creation of an entirely new household cleaning product category.
In this particular assessment, the management has a higher tolerance for risk, is entrepreneurial and sees a strategic fit for the new household cleaning product. However, there are still some gaps in the area of partnerships to fill gaps in specific areas of expertise resulting in lower levels of flexibility.
The market is seen as competitive with low value added products and lower margins but showing potential for strong growth. Moreover, the company has well developed contacts and existing networks to accelerate the launch of the new household cleaning product.
The technical review indicates that this is an area of strength and that, combined with high compatibility with other systems, could accelerate spin off products in the future.
The financial assessment indicates that the company has positive cash flow, adequate internal capital requirements and the resources to grow the operation. However, there are gaps in the financial commitment of external partners which may not meet the ROI requirements of external investors.
To determine the product sales potential of the new household cleaning product, it is important to evaluate the market potential based on five key considerations:
- Size of the market- how many units are sold in the product category?
- Value of the market- what is the dollar value of all products sold in the product category?
- Purchase frequency- how often is the product purchased by consumers
- Competition – how many players are in this market
- Price- what is the price point that is likely to generate consumer interest?
Once these assessments are completed, it will be important to consider three scenarios – good/better/best revenue forecasts for the product.
The next step is to consider options for Bringing Your Product to Market. This question needs to be answered early in the product development process: What vehicle will I use to bring my product to market?
Commercialization options range from selling the technology you are in the process of developing outright to starting your own company to bring the product to market. Before moving ahead with a particular product development project, it is important to review all the commercialization options available.
Expenditures
Customer’s Cost
When evaluating a new product or service, it is prudent to calculate the costs for design, development and marketing as well as to develop some expectations for market penetration and sales. This is a rational approach to the business of developing products and services.
Still, there are firms that fail to develop a consistent internal cost model, and have little understanding or knowledge of the importance of understanding the cost of acquisition, and use of a new product or service from a consumer’s point of view. Under expenditures, three important considerations have been identified, specifically, Market Research & Technical Feasibility, Product Development & Testing and Production & Market Launch.
Impact of Open Source on Small Business
- Market Research & Technical Feasibility costs
Market Research & Technical Feasibility costs may include Project Management Training/Consulting, Focus Group Costs, Product mock-up costs and Legal/Professional fees.
What information do I need?
- Project Management Training/Consulting
- Other HR training costs
- Focus Group Costs
- Brochure Development
- [Costs to gather] market intelligence
- Product mock-up costs
- Staffing Costs
- Consulting Costs (idea assessment, marketing assistance)
- Technical Review of Product Concept (Lab)
- Legal/Professional fees
- Trade Show attendance or end-user visits
Use this section of the worksheet to estimate your Market Research & Technical Feasibility costs. In the sample below, the Market Research & Technical Feasibility costs are relatively high and at times almost half of the operating cost.
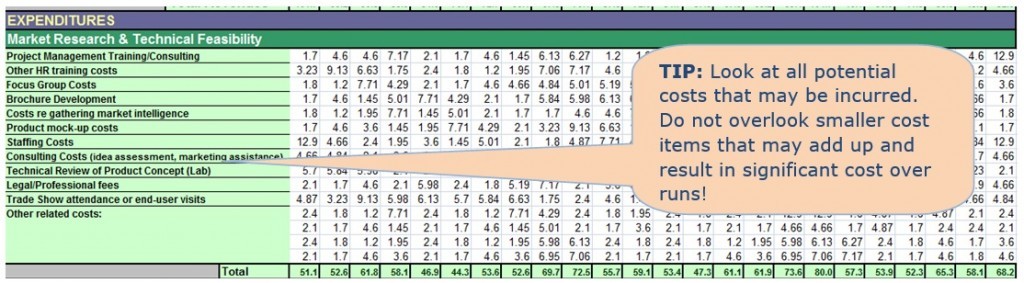
TIP: There may be many other items that require review such as Application Fees, Legal Fees, IP and Packaging Design costs.
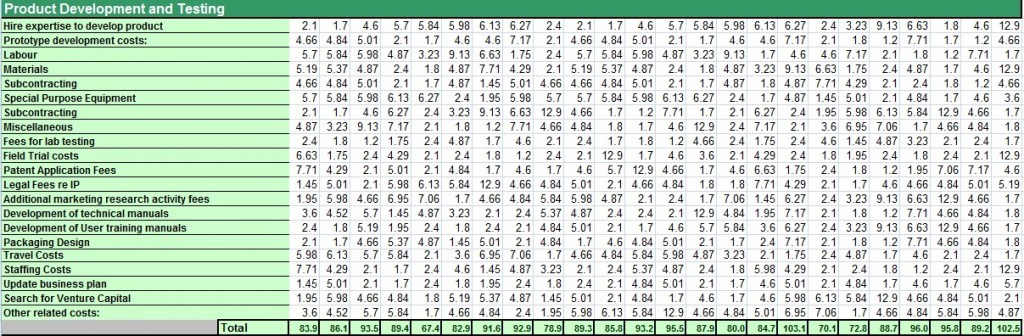
- Product Development & Testing costs
Product Development & Testing costs relate to 19 items that could impact this area. Specifically, those items include product development costs, subcontracting, materials and lab testing fees. The product development and testing component is crucial to the innovation process and requires added attention due to the significant impact the outcome of this stage will have on schedules, costs and the overall success of the innovation initiative.
What information do I need?
- Hire expertise to develop product
- Prototype development costs:
- Labour
- Materials
- Subcontracting
- Special Purpose Equipment
- Subcontracting
- Miscellaneous
- Fees for lab testing
- Field Trial costs
- Patent Application Fees
- Legal Fees
- Additional marketing research activity fees
- Development of technical manuals
- Development of User training manuals
- Packaging Design
- Travel Costs
- Staffing Costs
- Update business plan
- Search for Venture Capital
Use this section of the worksheet to estimate your Product Development & Testing costs. Click on the image to see the sample worksheet. In the example below, the legal fees related to IP are relatively higher because of the proprietary nature of the product ingredients and also the packaging uses a unique spill proof shape that can potentially be patented.
- Production & Market Launch costs
Production & Market Launch costs include over sixty items that are clustered under four major areas of start-Up Costs (for new operation), Production Facilities, Marketing and Operating Budget (New Start-up) costs.
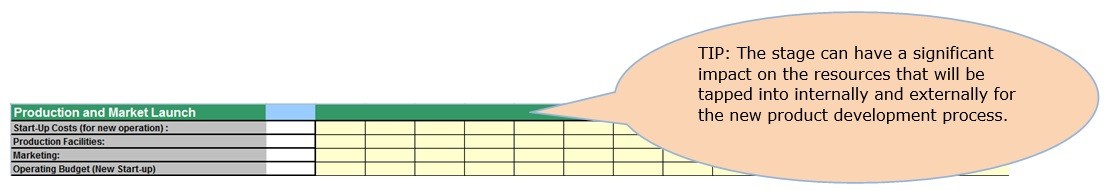
3a. Start up costs
The first item under Production and Market launch costs is start-up costs. This relates to specific situations where the product is being launched by an organization in a start up phase.
What information do I need?
- Legal fees & expenses to establish the new organization
- Consulting fees to develop trade name & trademark
- Legal fees & expenses to establish trade name & trademark
- Accounting fees for establishing accounting system
- Staff recruitment expenses
- Office renovations & related expenses
- Office stationery & supplies
- Signs & related purchase & installation
- Office furniture & fixtures purchase & installation
- Telephone & related equipment purchase & installation
- Computer & networking equipment purchase & installation
- Computer software purchases & installation
- Vehicle & related acquisition costs
Use this section of the worksheet to estimate your Start up costs:
3b. Production Facilities
The benchmark for production facility related costs will offer useful guidelines on whether some or all of the production should be managed in-house or outsourced.
What information do I need?
- Acquisition costs of technical & production space
- Renovation of technical & production space
- Design of production systems & equipment
- Technical equipment purchase & installation
- Production equipment purchase & installation
- Tooling (e.g. dies, moulds) purchases & expenses
- Technical & production supplies & related
- Packaging tooling and related purchases & expenses
TIP: Outsourcing part of the production will have a significant impact on the production space costing component and also capital costs related to production equipment.
Use this section of the worksheet to estimate your Production Facility costs:
3c. Marketing
Marketing can also a significant variable cost item due to the need for targeted strategies to increase awareness of products among specific consumer groups. Variables include PR, E-commerce, Advertising and other promotional expenses.
What information do I need?
- Marketing consulting (e.g. development of marketing tools)
- Development & negotiation of distribution arrangements
- Product market launch expenses
- Press release program expenses
- E-commerce strategy & design consulting
- Internet site development expenses
- Company &/or product brochure
- Promotional materials (e.g. product video)
- Trade show exhibit fixtures & materials
- Development and negotiation of supplier agreements
Use this section of the worksheet to estimate your Marketing costs:
3d. Operating Budget
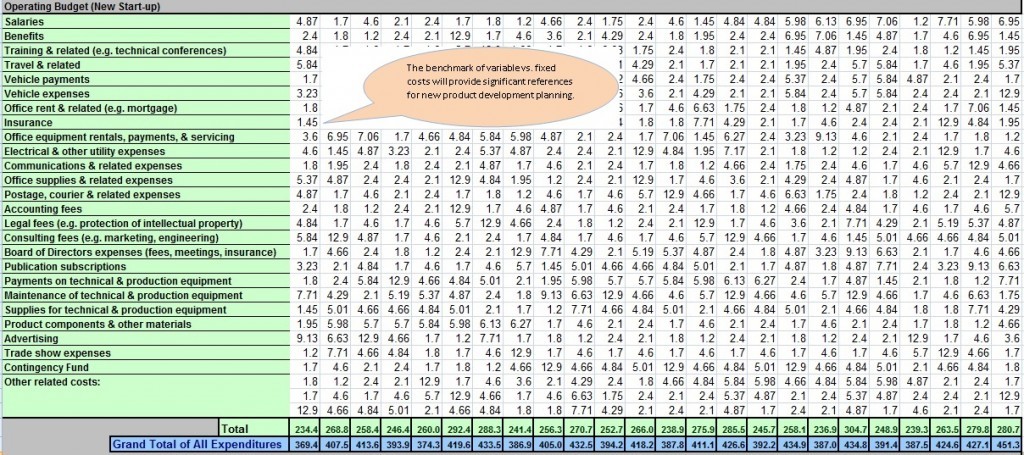
The operating budget consists of fixed costs – costs that include items such as salaries and benefits, training, utilities and legal fees. These costs need to be carefully planned and accounted for in projections as high operating costs can erode the financial flexibility of an organization to redirect funds to increase resources available to innovation initiatives such as new product development.
What information do I need?
- Salaries
- Benefits
- Training & related (e.g. technical conferences)
- Travel & related
- Vehicle payments
- Vehicle expenses
- Office rent & related (e.g. mortgage)
- Insurance
- Office equipment rentals, payments, & servicing
- Electrical & other utility expenses
- Communications & related expenses
- Office supplies & related expenses
- Postage, courier & related expenses
- Accounting fees
- Legal fees (e.g. protection of intellectual property)
- Consulting fees (e.g. marketing, engineering)
- Board of Directors expenses (fees, meetings, insurance)
- Publication subscriptions
- Payments on technical & production equipment
- Maintenance of technical & production equipment
- Supplies for technical & production equipment
- Product components & other materials
- Advertising
- Trade show expenses
- Contingency Fund
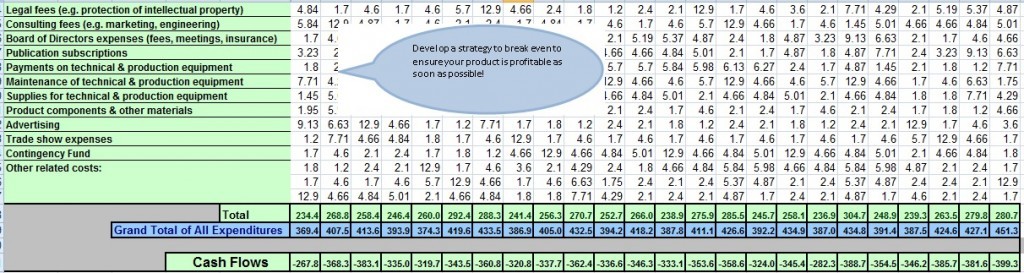
Use this section of the worksheet to estimate your Operating Budget. In the example, of the chocolate product below, the operating budget is fairly stable- a good sign, indicating that it may be possible to make longer projections about the success of the innovation.
Congratulations on completing your costing summary!
Now calculate the Grand Total of All Expenditures. If revenue is above expenses in the calculations, that’s an excellent outcome. However, if revenue projections are below expenditures, as in the example of the household cleaning product below, that should not be a significant concern in the initial launch phase. Most innovation or new business initiatives incur losses in the initial years because of significant upfront investments and setting up costs.